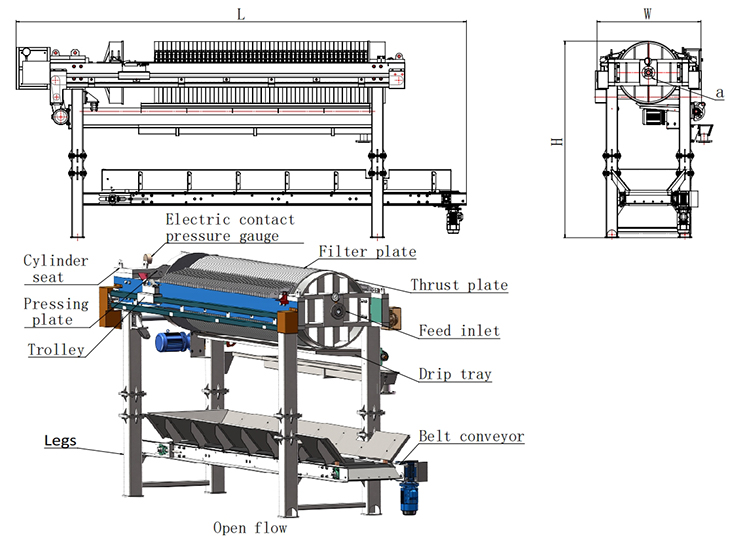
Customizable Heavy Duty Circular Filter Press for Solid Liquid Separation
Key Features
1.High-strength circular filter plate design, with uniform force distribution and excellent pressure resistance performance
2.Fully automatic PLC control system, enabling one-click operation
3.Modular structure design, with simple and quick maintenance capabilities
4.Multiple safety protection devices ensure reliable operation
5.Low-noise design, in line with environmental protection requirements
6.Energy-saving and highly efficient, with low operating costs.
Working Principle
1.Feed stage: The suspension passes through the feed pump and enters the filter chamber. Under the pressure, the liquid passes through the filter cloth and flows out, while the solid particles are retained and form a filter cake.
2.Compression stage: The hydraulic or pneumatic system applies high pressure, further reducing the moisture content of the filter cake.
3.Discharge stage: The filter plates automatically open, the filter cake falls off, and the solid-liquid separation is completed.
4.Cleaning stage (optional): Automatically clean the filter cloth to ensure filtration efficiency.
Core Advantages
✅ High-strength Structure: The circular filter plate distributes the force evenly, can withstand high pressure (0.8 – 2.5 MPa), and has a long service life.
✅ Efficient Filtration: The moisture content of the filter cake is low (can be reduced to 20% – 40%), reducing the cost of subsequent drying.
✅ High Automation Level: Controlled by PLC, it automatically presses, filters, and discharges, reducing manual operations.
✅ Corrosion-resistant Materials: The filter plate can be made of PP or stainless steel 304/316, suitable for acidic and alkaline environments.
✅ Energy-saving and Environmentally Friendly: Low energy consumption design, the filtrate is clear and can be reused, reducing wastewater discharge.
Main application industries
Mining and Metallurgy: Metal ore dehydration, coal sludge treatment, tailings concentration.
Chemical Engineering: Solid-liquid separation in areas such as pigments, catalysts, and wastewater treatment.
Environmental protection: Dewatering of municipal sludge, industrial wastewater, and river sediment.
Food: Starch, fruit juice, fermentation liquid, extraction and filtration.
Ceramic building materials: Dehydration of ceramic slurry and waste stone materials.
Petroleum energy: Drilling mud, treatment of biomass sludge.
Others: Electronic waste, agricultural manure dehydration, etc.